Responsible Marketing Corporate Sustainability Disclosures

Responsible marketing– ensuring marketing activities are reliable and truthful – is a growing area of scrutiny from regulators and investors alike. Protecting consumers and building trust are foundational, but expectations for responsible marketing now extend to demonstrably principled and transparent practices and disclosures.
A Growing Business Imperative
This increased focus is reflected in evolving legal frameworks. Jurisdictions like Canada and the United States have existing regulations addressing responsible marketing, particularly concerning the protection of children, the accuracy of environmental and health claims, and data privacy. The European Union’s European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS) formally recognize responsible marketing as a potentially material topic within “ESRS S4 – Consumers and End-Users,” signaling its growing importance for companies operating in or reporting to the EU.
Investors are also paying attention. The Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) identifies responsible marketing practices as a potentially material sub-topic within “Selling Practices & Product Labelling.” The SASB standards flag this issue as potentially material for multiple industries, including Commercial Banks, Alcoholic Beverages, and Healthcare Delivery, indicating investor concern around risks associated with misleading or unethical marketing in these sectors. This recognition demonstrates that responsible marketing is increasingly viewed as a key indicator of a company’s broader sustainability performance and risk management.
Trends in Disclosures and Controversies
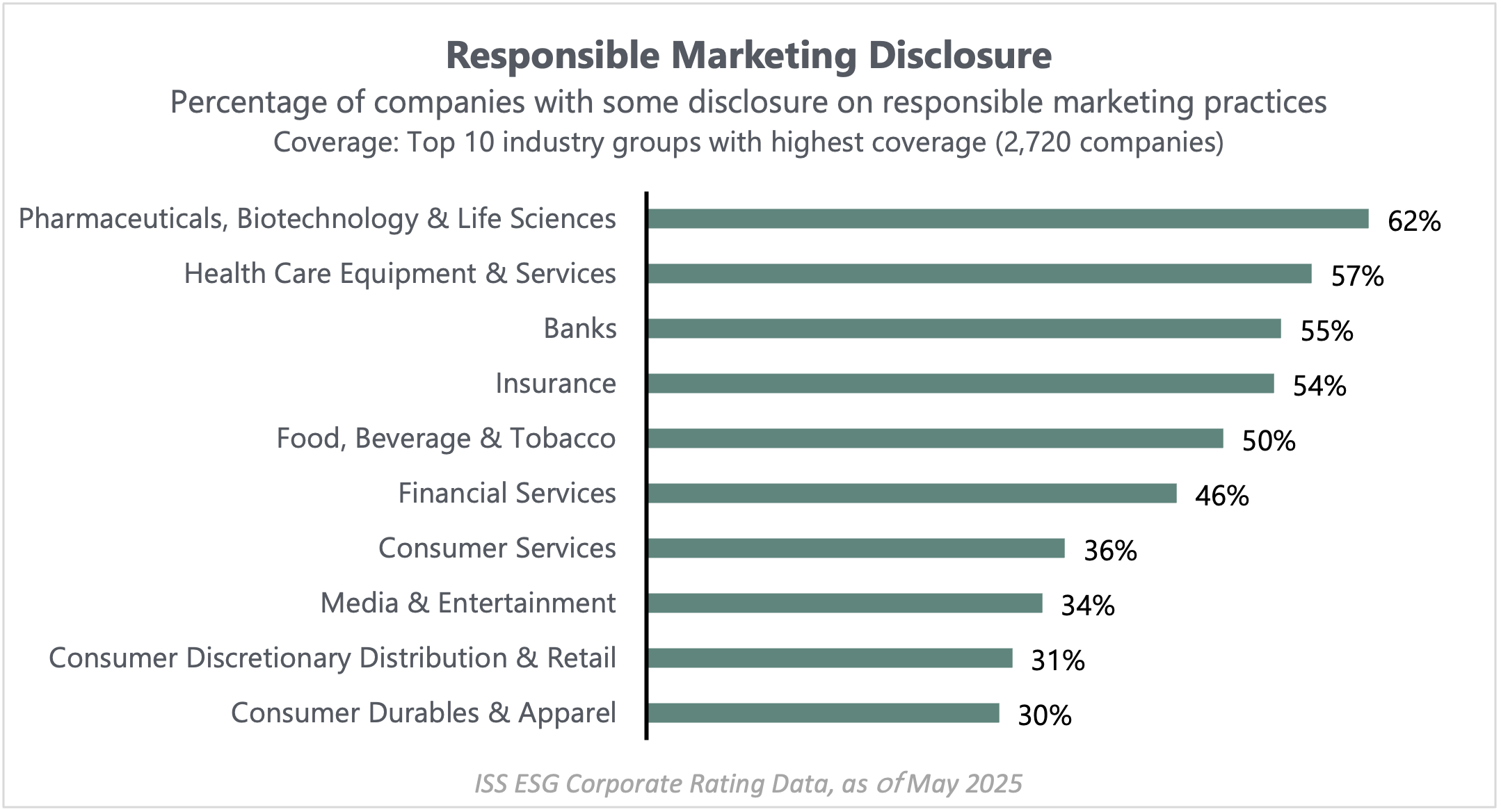
ISS-Corporate recently analyzed public disclosures regarding responsible marketing practices across a range of industries. As the graph below illustrates, the percentage of companies openly addressing responsible marketing policies varies significantly, particularly within sectors where this issue is most critical. Our analysis focused on 3,342 companies – those included in the ISS ESG Corporate Rating assessment for responsible marketing, drawn from our broader coverage of over 8,100 companies globally. We identified the ten industry groups with the largest number of companies assessed on this indicator and ranked them by the proportion demonstrating some level of disclosure.
The resulting rankings, visualized in the graph below, reveal a clear divergence in disclosure rates. Industries like Pharmaceuticals, Healthcare Equipment, and Banks demonstrate the strongest commitment to transparency, with the highest percentage of companies disclosing some form of responsible marketing policy. This pattern suggests increasing awareness and responsiveness to both investor scrutiny and emerging regulatory expectations in these key sectors.
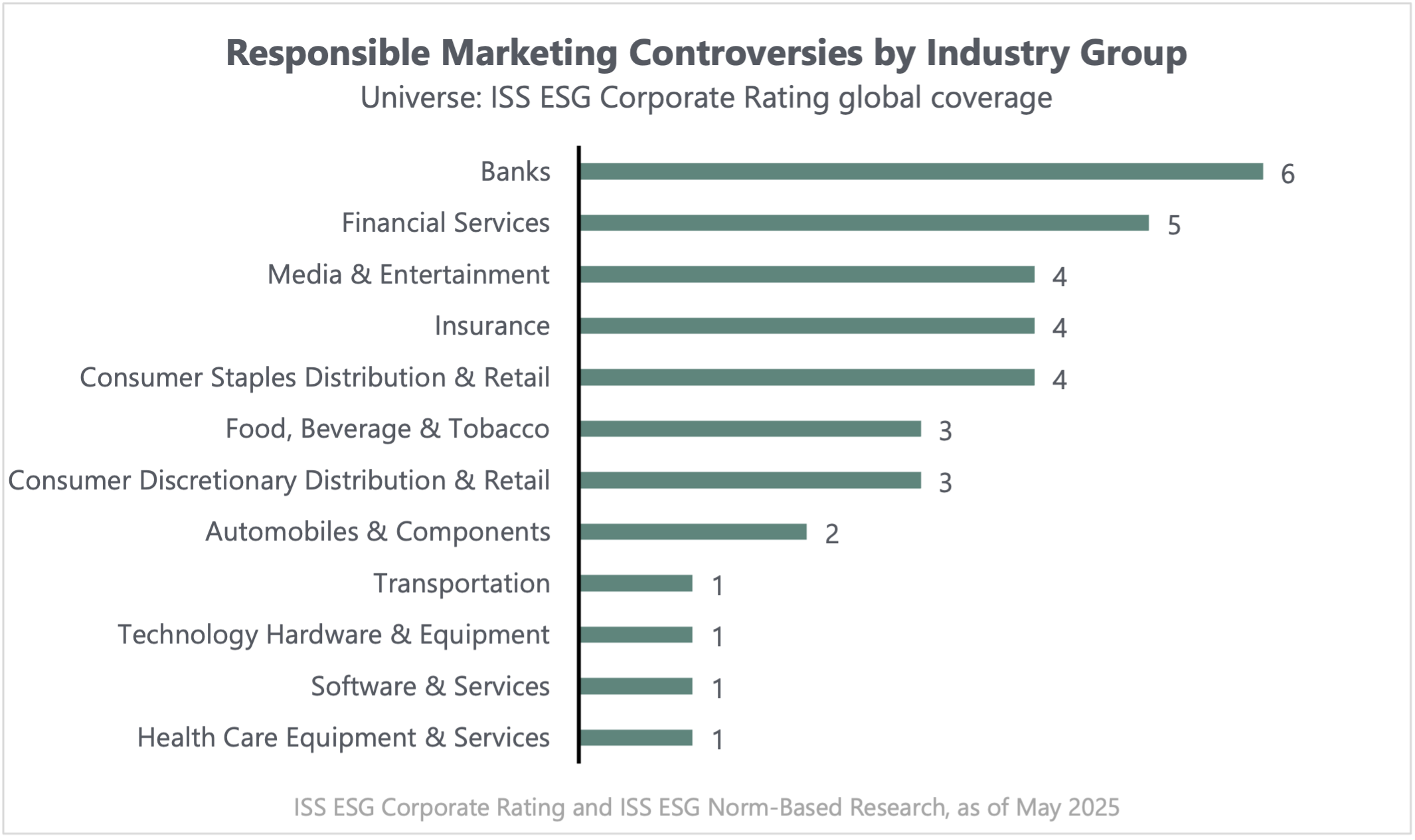
ISS-Corporate also analyzed the prevalence of responsible marketing controversies in the covered universe, utilizing our Norm-Based Research methodology. This research assesses potential violations of international norms – guided by frameworks like the UNGC, UN GPHR, and OECD Guidelines – and evaluates how companies manage related controversies, considering the severity of impacts, verification levels, and remediation efforts, through monitoring of diverse sources including media, NGOs, and governmental agencies. Importantly, the data indicates that significant controversies are relatively rare and only flagged when they meet a predetermined threshold of concern.
As shown in the graph, Banks and Financial Services experience the most responsible marketing controversies, likely due to the heavily regulated nature of the industry and the potential for issues around data privacy, fair lending practices, and transparency in financial products. Media and Entertainment may see a higher incidence of controversies related to misinformation or inappropriate content targeting vulnerable audiences, while consumer sectors like Food, Beverage & Tobacco often face scrutiny regarding the marketing of potentially harmful products and misleading health claims.
Best Practices in Responsible Marketing
Strong responsible marketing practices can be formalized through responsible marketing policies. While the content of these policies varies slightly across industries, several key themes emerge as best practices.
- Adherence to International Frameworks and Guidelines: The International Chamber of Commerce’s (ICC) Advertising and Marketing Communications Code establishes best practices applicable to all forms of advertising and marketing, including those created by Artificial Intelligence (AI). Based on four main principles – legality, decency, honesty, and truthfulness – the Code has been deployed globally for over 80 years. Other industry-specific frameworks, such as the International Federation of Pharmaceutical Manufacturers and Associations’ (IFPMA) Guiding Principles on Ethical Conduct and Promotion, may also inform responsible marketing policies.
- Commitment to Identifiability and Substantiation: Companies prioritizing responsible marketing practices commit to clear, truthful labeling on products and refrain from making unsubstantiated claims about their business. Best practices in this regard vary by industry. For example, in the financial sector, robust policies often include commitments to transparent pricing, risk disclosure, and avoidance of fine print.
- Protection of Consumers: For commercial products, particularly in the food and beverage sector, strong responsible marketing policies often commit to standards of decency, such as a commitment to respect human dignity or a commitment against promoting discriminatory items. Similarly, comprehensive policies frequently pledge to protect children and safeguard human health – both of which are potentially material sub-topic areas within ESRS S4 – Consumers and End-Users. In the pharmaceutical and healthcare equipment industries, leaders in responsible marketing commit to promoting only approved products and refrain from advertising until safety is established.
Technological innovations that open access to a wide array of consumers, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, make responsible marketing practices a key element of robust corporate governance for many organizations.
Strong responsible marketing practices not only ensure regulatory compliance but also position a corporation as a leader in transparency and as a champion for the interests of both consumers and shareholders.
Climate Action 100+: Trends and Expectations for 2026
EU Sustainability Rules Reset: What the 2026 Changes Mean
Science-Based Targets: Evolving Standards and Global Adoption
Latin America’s Sustainability Reporting Gains Momentum
Rare Earth Minerals: The Hidden Backbone of the Energy Transition
California Climate Laws Update: CARB Workshop and SB 261 Pause
Energy Management Systems: Global Trends and Best Practices
2025 Sustainability Reporting: Global Trends in Framework Adoption
Getting Materiality Right: Challenges, Risks, and Best Practices
Spain Introduces Mandatory Climate Disclosure